Attribute Grammers
2020-07-23 |- Attribute grammers ==> based on context free grammer
- State additional grammers for context free grammers
- Attribute Grammer = CFG + attributes (piece of informations) + semantics actions (actions of functions, how the values are produced) + predicates (boolean value functions)
Static Semantics
- The additional features that are described by attribute grammars are called as the static semantics
- Example: Detect variable not declared yet.
- About synactic structure
Attributes
Variables associated with grammar symbols. (information pass through parse tree)
- Synthesized: A symbol depend on the attributes of its children.
- Inherited: Depends on the attributes of its parent and its siblings.
We will try to describe this rule but context free grammer is not enough.
Semantic Functions | Actions
- The additional features that are described by attribute grammars
- Described by CFG
Dynamic Statics
- Run-time
- Described by natural language
CFG example:
<exp> -> <num> + <num>
<num> -> tNUM
Implementation
Example
Postfix expressions.
1 ==> translated to 1
1 2 + 3 4 - + ==> translated to 2
Attribute grammers uses for: * Describe additional syntactic properties * For translation
Context Free Grammer
<expr> -> tNUM
| <expr> <expr> +
| <expr> <expr> -
so the first step is drawing the tree.
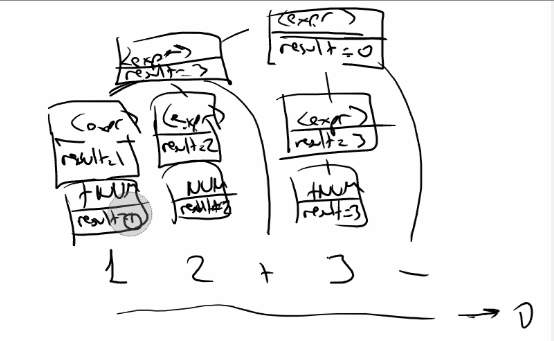
We added : - Result attribute
 This was the end of the blog post. You can reach me via email umusasadik at gmail com
This was the end of the blog post. You can reach me via email umusasadik at gmail com